Table of Contents
Introduction:
Cervical cancer is a type of cancer that occurs in the cells of the cervix, the lower part of the uterus connecting to the vagina. It is a significant health concern for women worldwide, but with proper awareness, screenings, and vaccinations, the risk of developing cervical cancer can be significantly reduced.
Causes and Risk Factors:
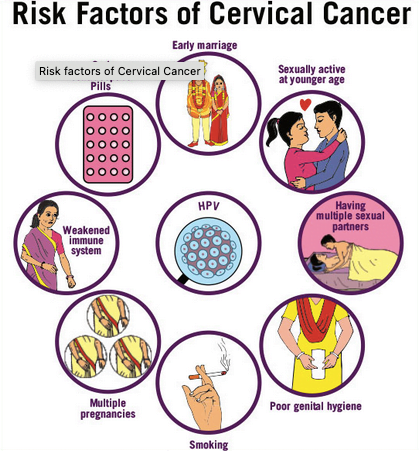
What are the risk factors?
- Human Papilloma Virus (HPV) infection
- Early Marriage
- Sexually active at younger age
- Having multiple sexual partners
- Poor genital hygiene
- Smoking
- Multiple pregnancies
- Weakened immune system
- Malnutrition
- Prolonged use of Oral Contraceptive Pills (OCPs)
Understanding the Female Reproductive System
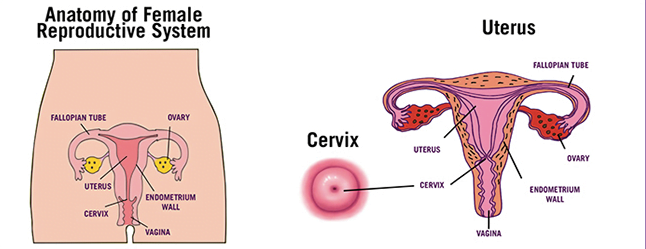
Deconstruction of womanish Reproductive System The organs in the womanish reproductive system include the uterus, ovaries, fallopian tubes, cervix, and vagina. The uterus is concave, pear- shaped organ where a foetus grows. The cervix is the lower, narrow end of the uterus connecting the body of the uterus to the vagina( birth conduit). The lower part of the cervix( ecto cervix) lies within the vagina and the upper two- thirds of the cervix( endo cervix) lies above the vagina. utmost cervical cancers appear in the area where the endo cervix and ecto cervix join.
Are you looking for jobs in CANADA ? 10 Prime jobs avaiable in CANADA in 2024! APPLY NOW
Causes and Risk Factors:
Cervical cancer is primarily caused by patient infection with high- threat strains of the mortal papillomavirus( HPV). HPV is a common sexually transmitted infection, and certain strains can lead to the development of cervical cancer over time. Other threat factors include a weakened vulnerable system, smoking, long- term use of birth control capsules, and a family history of cervical cancer.
Cervical Cancer Symptoms:
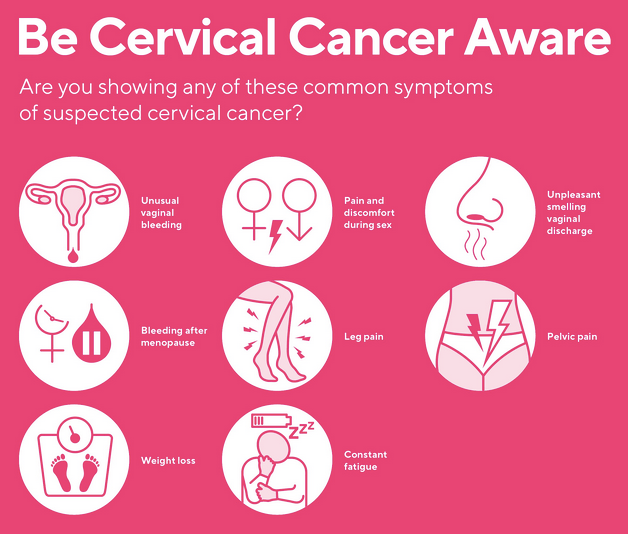
Women with pre-cancers and early cervical cancers usually have no signs and symptoms. Signs & symptoms of CC appear only after the cancer has reached an advanced stage. More severe symptoms may develop at advanced stages of CC.
- Irregular, inter-menstrual (between periods) bleeding.
- Abnormal vaginal bleeding after sexual intercourse and a pelvic examination or bleeding after menopause.
- Vaginal discomfort or odorous discharge from vagina, the discharge may contain some blood and may occur between periods or after menopause.
- Pain during sex
- Back, leg or pelvic pain.
- Fatigue, weight loss, loss of appetite.
- Swelling in one leg.
Stages of cervical cancer:
The stage of cervical cancer indicates how big it’s and whether it has spread to other areas of your body. Knowing which carry you have helps your croaker produce the most effective treatment plan for you and gives you some idea of your prognostic.
The stage of cervical cancer is determined by the results of a physical test, necropsies and imaging.
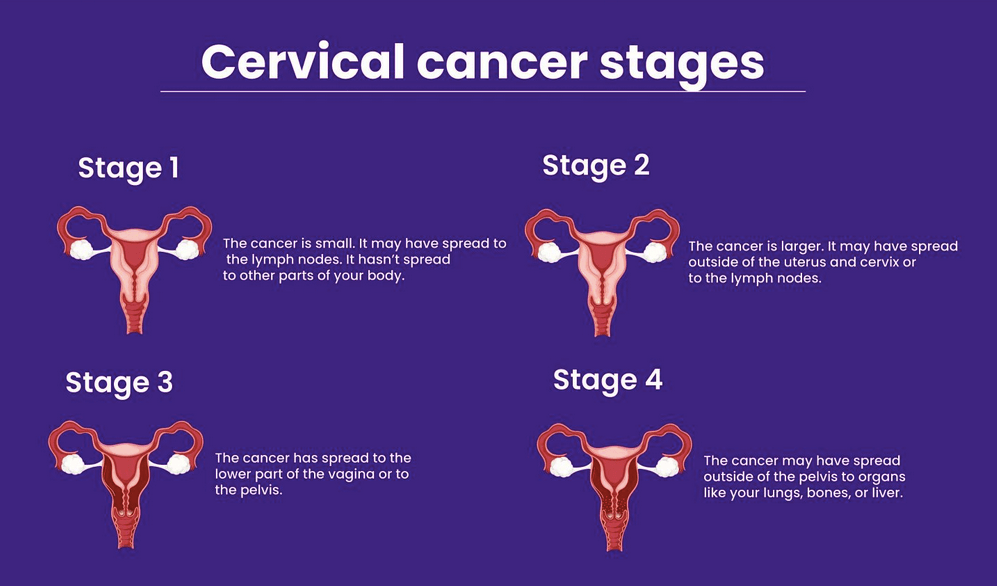
The stages of cervical cancer are
Stage 1 – The cancer cells are only within the cervix .
Stage 2 – The cancer has spread from the cervix into the upper part of the vagina or the apkins girding the cervix.
Stage 3 – The cancer has spread to the lower part of the vagina, into the pelvic wall or to near lymph bumps.
Stage 4 – The cancer has spread into the near body organs similar as the bladder or bowel, or has spread further in the body to areas similar as the lungs, liver or bones.
Screening and Diagnosis:
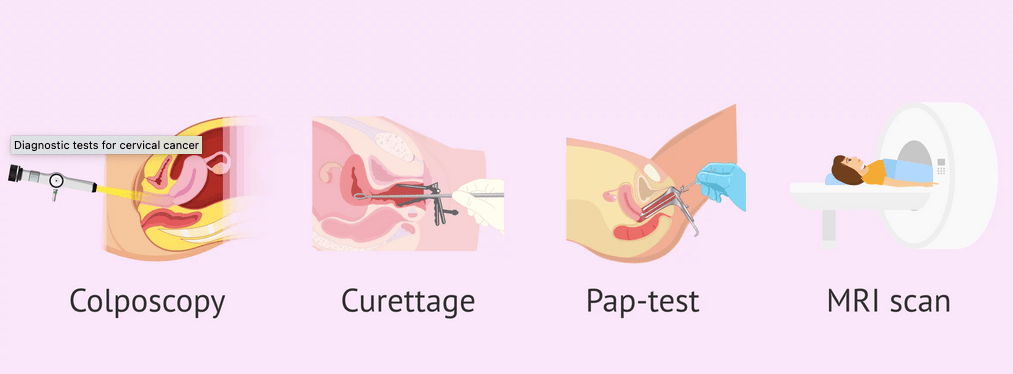
Regular Pap smears and HPV tests are essential for the early detection of cervical abnormalities and the presence of HPV. Pap smears involve collecting cells from the cervix, which are then examined for any abnormal changes. If abnormalities are detected, further diagnostic tests such as colposcopy and biopsy may be performed to confirm the diagnosis.
- Regular Pap smears
- HPV tests
- Colposcopy
- Biopsy
Are you looking for jobs in CANADA ? 10 Prime jobs avaiable in CANADA in 2024! APPLY NOW
Prevention:

Preventive measures play a crucial role in reducing the risk of cervical cancer. The HPV vaccine is a powerful tool for preventing infection with the most common high-risk HPV strains. It is recommended for both males and females before they become sexually active. Additionally, practicing safe sex, quitting smoking, and maintaining a healthy lifestyle can contribute to reducing the risk of cervical cancer.
- HPV vaccine
- Practicing safe sex
- Quitting smoking
- Maintaining a healthy lifestyle
Key Message: All women aged 30 years and more should be screened for CC at least once.
Treatment:
Cervical cancer is often treatable.

The type of treatment demanded for cervical cancer depends on the type, stage and size of the cancer, as well as your general health. Your croaker and specialists will concoct a personalised plan for you, which may include one, or a combination of the following:
Surgery for cervical cancer
There are several types of surgery used to treat cervical cancer. These can include
The junking(removal) of part of the cervix
Junking(removal) of the cervix and upper part of the vagina
Junking(removal) of the cervix and womb( hysterectomy)
Junking(removal) of the cervix, womb, ovaries and fallopian tubes, and all or corridor of the bladder, bowel, vagina or rectum
If the cancer has spread to your lymph bumps you may also need to have these removed.
Chemotherapy for cervical cancer
Chemotherapy uses strong specifics to kill cancer cells. It’s frequently given alongside radiotherapy to shrink the cancer, after surgery to help stop the cancer from coming back or to treat advanced cancer that has comeback or spread to other corridor of your body.
Radiotherapy for cervical cancer
Radiotherapy uses high- energy shafts of radiation to kill cancer cells. This type of treatment may be used if your cancer is large or has spread, after surgery to help stop the cancer from coming back or to help ameliorate symptoms, like bleeding.
Targeted medicine curatives for cervical cancer
Certain specifics are used in the treatment of advanced cancer to help shrink it or stop it from getting any larger.
Conclusion:

Cervical cancer is a significant health issue, but with awareness, early detection, and preventive measures, its impact can be minimized. Regular screenings, vaccination against HPV, and adopting a healthy lifestyle are key steps in reducing the risk of developing cervical cancer. By promoting awareness and understanding, we can empower individuals to take charge of their reproductive health and work towards a future with fewer cases of cervical cancer.
Global Vaccination Initiatives:
Various global health organizations and governments have implemented vaccination programs to increase access to the HPV vaccine, particularly in low- and middle-income countries. These initiatives aim to ensure that women worldwide have the opportunity to benefit from this preventive measure, thereby contributing to the global fight against cervical cancer.
HPV VACCINE COST: Cervavac’s two dose vial is available for ₹4,000, of which one dose costs ₹2,000